10 Reasons You're Biting Your Tongue In Your Sleep

In this article, we may include products or services we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission to help fund our mission to create more healthy smiles. Here’s our process.
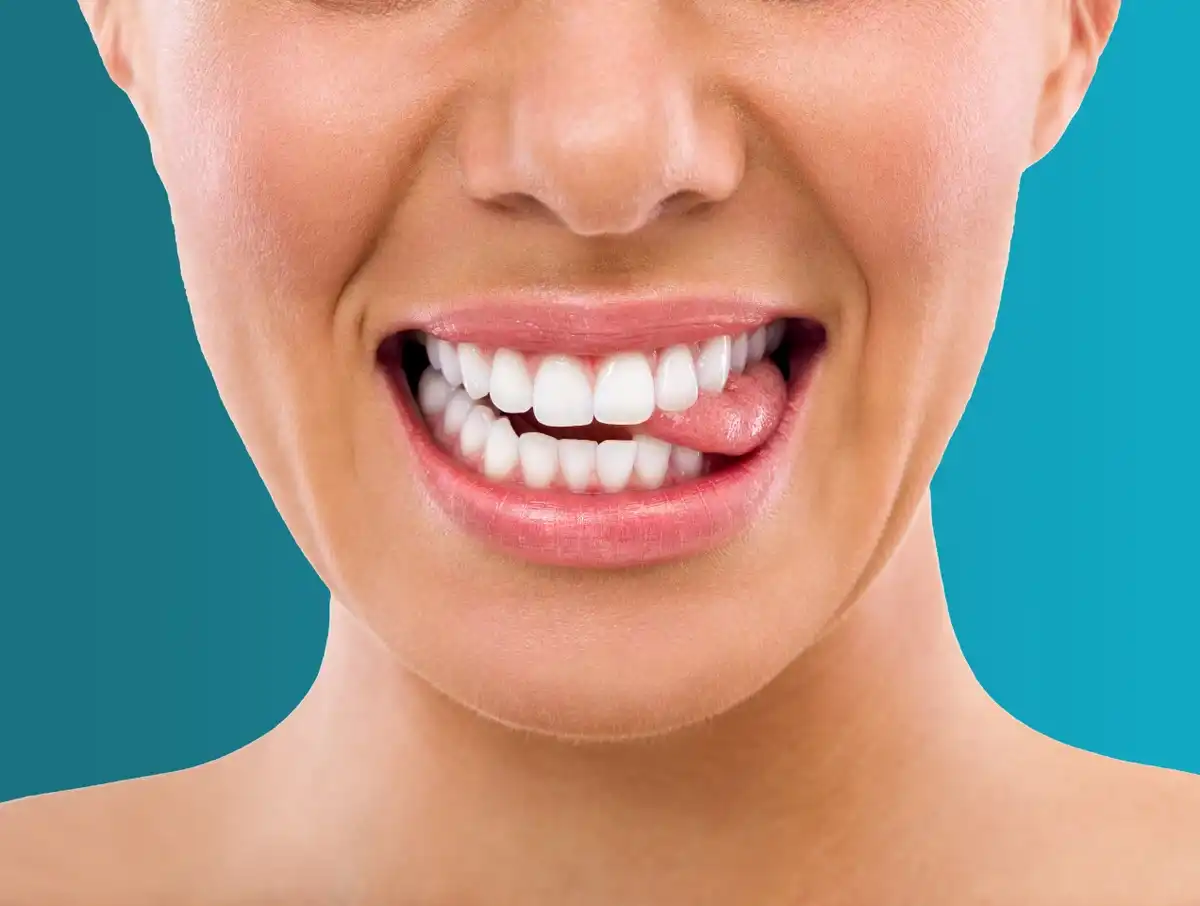
Some people have scalloped edges along the sides of their tongue, caused by tongue biting. Even though you probably don’t bite your tongue on purpose or out of habit, it can still happen during everyday activities. Or you might be biting your tongue when you sleep (nocturnal tongue biting.)
The way your tongue looks can say a lot about underlying health issues, the way you sleep, and how your jaws line up. So, if you notice signs of nighttime tongue biting, be sure to talk to your dentist.
Common Symptoms of Tongue Biting
All of the biting and chewing on your tongue basically toughens the skin in those places, creating what you might think of as a callous elsewhere on your body. That’s why the chewed areas are white and a bit firmer than the pink tongue tissue around them.
What Could It Be? Causes Of Tongue Biting
1. Malocclusion
Symptoms
A malocclusion can include crossbites, gaps between teeth, crowding, or any other condition where the teeth don’t line up properly. TMJ pain is also common.
Treatment
Braces or clear aligners will help bring your teeth into a proper occlusal relationship, eliminating the risk of misaligned teeth consistently biting your lips, cheeks, or tongue.
2. Anxiety
High-stress levels or anxiety can cause us to clench our teeth together during the day or even while we’re sleeping. Anxiety can cause someone to bite their tongue during sleep unknowingly.
Symptoms
Someone with severe anxiety may experience headaches, sore gums, stomach issues, difficulty concentrating, or depression. Many of us handle our anxiety in different ways, so it can be challenging to diagnose at times. And in a post-pandemic world, more of us have issues with some extent of anxiety than we ever did before.
Treatment
Cognitive behavioral therapy/counseling can be extremely helpful with managing anxiety. So can exercise and meditation. Medication is also available when needed.
3. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding and Clenching)
Symptoms
People who suffer from bruxism tend to have flat, worn, or broken teeth. They also experience frequent headaches, TMJ issues, and ear pain.
Treatment
Since bruxism is caused by different things, treatment can range from braces to getting a nightguard. The key is to establish a proper biting relationship while easing muscle tension in your mouth.
Related: 5 Best Night Guards for Teeth Grinding
4. Rhythmic Movement Disorder
Symptoms
Rhythmic movement disorder causes repeated body movements. Such as moving the tongue, or chewing motions. It’s usually most obvious in the head and neck or trunk of the body.
Treatment
Medications and/or headgear are common. Working with a neurologist is key.
5. Nighttime Seizures
Symptoms
Individuals that experience nighttime seizures may have severe lesions inside of their mouths, including large cuts in their tongue from biting down on it in the middle of a seizure.
Treatment
Along with working with your medical specialist to control/manage nocturnal seizures, speak to your dentist about getting fitted with a professional-grade mouthguard to wear when you sleep.
6. Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea originates in the mouth. Or rather, the back of it. Hence why your dentist can screen for and help treat sleep apnea symptoms with special dental appliances to help stop tongue biting.
Symptoms
People who have obstructive sleep apnea tend to experience a lot of flat, worn, or broken teeth, as well as bite marks on the sides of their tongues.
Treatment
7. Facial Muscle Spasms
We can get muscle spasms anywhere in our body, including our face. They may be short-lived, or more of a persistent condition caused by nerve damage or viral infections. It can also be caused by anxiety or stress.
Symptoms
Involuntary facial motions including clenching in the jaws or mouth are common. Twitching jaw muscles is usually the most noticeable symptom.
Treatment
Botox injections provide natural muscle relaxing advantages to ease tension in the mouth, face, head, or neck. That’s why it’s frequently used to treat TMJ disorder!
8. Drug Use
Recreational drug use can cause major teeth grinding and cheek biting. Cocaine and Ecstasy are just two examples.
Symptoms
Drug-induced bruxism is a common side-effect of recreational and illicit drug use. The individual may tend to clench and grind their teeth (biting their tongue in the process) when high. We also see a high rate of cavities in people who use drugs, because of the dry mouth and sugar intake that tends to accompany their habit.
Treatment
Rehabilitation programs can help people come off drug dependencies. Cognitive behavioral therapy is usually a must.
9. Lyme Disease
Symptoms
Teeth clenching and grinding is an extremely common symptom of Lyme disease. As are TMJ dysfunction, headaches, and a skin rash.
Treatment
Recovering from Lyme disease can take months or years in some cases. Antibiotic therapy is usually recommended.
10. Enlarged Or Swollen Tongue
Symptoms
Dry, cracked lips and bite marks along the sides and front of the tongue.
Treatment
There is no treatment for enlarged tongues, but there are therapies available for some of the medical conditions that contribute to swollen tongue tissue. Sleeping in a nightguard is extremely helpful to prevent biting your tongue.
Preventing Tongue Biting During Sleep
There are two important things you need to do if you’re constantly biting your tongue at night.
First, get a mouthguard or nightguard. Preferably one that’s fitted by your dentist. These custom appliances protect your teeth, tongue, and TMJ. Even if you do clench your teeth, the night guard will prevent you from damaging your tongue or tooth enamel. It’s better to wear through a mouthguard than it is your teeth.
Plus, during your dental exam, your dentist can have a peek around to see what’s going on. They’ll check how your teeth bite together, the muscles around your TMJ, and screen for other issues that may be contributing to all the tension in your mouth.
Your sleep study will tell your dentist or physician whether or not you have a sleeping disorder. If you do, you can get the right type of oral appliance to help with your sleeping AND stop your nighttime tongue biting.
See Your Dentist or Doctor
Chronic teeth clenching and tongue biting are classic warning signs of sleep apnea and a dangerous habit. But even tongue biting on its own can be painful. Especially if you’re biting the same area over and over because it stays swollen and never gets a chance to heal.
Dentists can fit you with the appropriate type of mouthguard or sleep apnea appliance. You cannot find those devices in a doctor’s office, online, or in a store. Since they are specially fitted for your mouth, they can only be delivered by a licensed dentist. If you’re already seeing a sleep physician, you can ask them to prescribe an oral sleep appliance and then fill that prescription at a local sleep dentistry office.
Oral sleep apnea appliances help manage sleeping disorders, snoring, and tongue biting. When they fit right, you may not even need a CPAP machine and can see results as early as the first night of use.
Getting fitted with the right type of mouthguard is important and not just for your tongue. It can prevent unnecessary and excessive wear to your tooth enamel or existing dental restorations. You’re essentially limiting your dental bills in the future, by preventing problems before they happen.
How To Stop Biting Your Tongue At Night
Can you tell that you’re tongue-biting whenever you sleep? Or do you catch yourself chewing on your tongue in the middle of the day out of stress? Talk to your dentist. Tongue biting may be a sign of something more serious. Without protective steps, you could also risk broken teeth or undiagnosed sleep apnea. Your dentist can screen for what’s causing your specific type of clenching or tongue chewing to help you determine the best way to get it under control. It might be as simple as fitting you with a protective mouthguard or ordering a home sleep study to screen you for a sleeping disorder.
Make your inbox smile!
Subscribe