Can You Really Die From A Tooth Infection?


Is it possible to die from a tooth infection? Hypothetically speaking, is there a timeframe for how long until a tooth infection kills you or puts you in the hospital? The answer might not be as simple as you think, but severe tooth infections can definitely be life-threatening.
Depending on how technical or knit-picky you want to get about the science behind it, yes, you can die from a tooth infection. Although by the time an infection reaches that severe of a level, it’s not just isolated inside of your tooth. It starts in your tooth but by the point it becomes fatal, there’s a lot more going on. All that being said, don’t ignore that cavity or a tooth abscess your dentist points out on your X-ray.
Can A Tooth Infection Kill You?
An infected tooth can kill you by allowing bacteria to spread elsewhere in your body. Especially your brain and bloodstream.
Let’s say for a moment that you have an abscessed tooth. These teeth have cysts around the root that are filled with bad bacteria. Slowly but surely, this cyst or tooth abscess will start to invade the bone structures and soft tissues next to the tooth. It could easily spread into your bloodstream, nasal sinuses, nerves, face, and yes, your brain.
Gum infections aren’t all that different. Even though there’s no tooth abscess there, you do have severe inflammation, bleeding, and colonies of bacteria living below the surface of your gum tissues.
Here are several life-threatening situations that can tie back to a toothache and why you shouldn’t skip out on that recommended dental work:
1. Sepsis:
2. Ludwig’s Angina:
3. Necrotizing Fasciitis:
4. Endocarditis:
5. Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis:
When you get a blood clot inside of the “cavernous sinuses” (like the hollow nasal sinuses above your teeth but below your brain and eye socket) it can be deadly. Since your tooth roots lie just alongside of some of your sinus cavities, you have to be especially careful about not allowing abscessed teeth to spread infection into those areas.
6. Osteomyelitis:
7. Brain Abscess:
How Long Until A Tooth Infection Kills You?
In reality, a person can die within days or weeks of a tooth infection spreading into their bloodstream. And since the severity of a dental infection isn’t easy to measure on your own without diagnostic X-rays, it’s extremely important to listen to your dentist’s recommendations when it comes to active dental disease. If you don’t trust your dentist or it seems like they’re recommending a treatment you don’t need, always, always, always get a second opinion. It just isn’t worth the risk of overlooking a potentially fatal tooth infection.
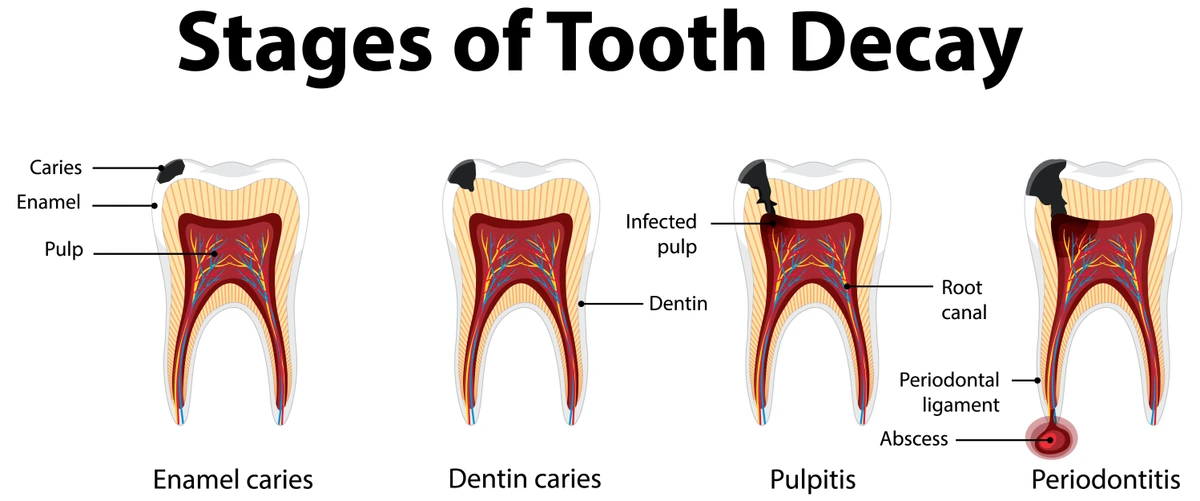
All of that being said, you’re most likely not going to die within a week of a small cavity being diagnosed. Why? Because tooth decay goes through various stages. Such as:
1. Enamel Decay
This is where the cavity is isolated in the outer layer of the tooth structure. A dental filling is usually all that’s needed.
2. Dentin Decay
Once the tooth decay has ruptured through the enamel, it enters into the softer dentin layer underneath. It can grow much more quickly at this point. Larger dental fillings are required. Or sometimes inlays, onlays, or crowns.
3. Pulp Decay
The tooth decay has reached the nerve tissue inside the tooth. At this point, root canal therapy is a must.
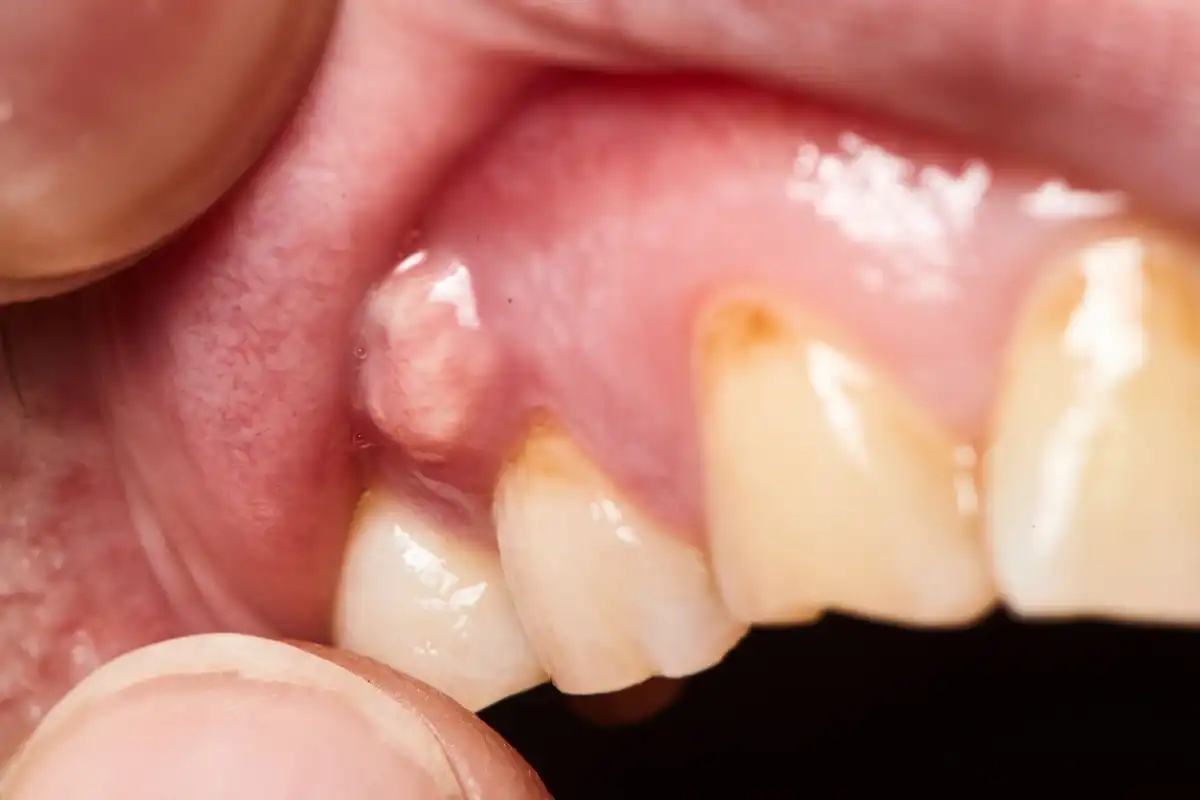
4. Dental Abscess Formation
A fluid-filled cyst develops around the tip of the tooth root. There may be a visible blister or pocket of pus on the gums. The cyst is visible inside the bone when an X-ray is taken. A root canal or extraction are imminent.
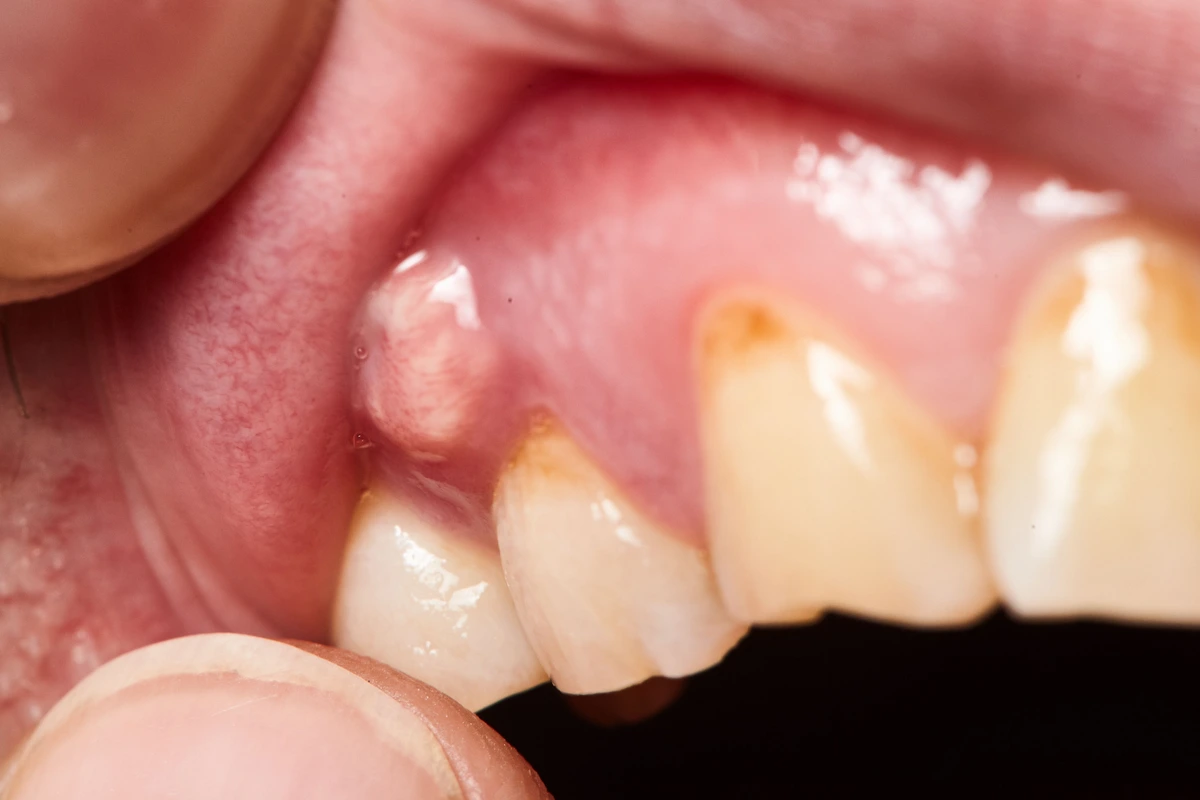
5. Serious Complications
Untreated abscessed teeth where the cyst spreads into the surrounding bone, sinuses, and blood vessels.
Symptoms of a Tooth Infection Spreading to the Body
In most cases, severe tooth infections are either related to an abscessed tooth or advanced periodontal disease. In both scenarios, redness and swelling of the mouth are extremely common. However, if the tooth infection has spread elsewhere in the face, you may notice a swollen cheek, jaw, eyes, throbbing pain or difficulty breathing due to an obstructed airway. Fatigue and fever are also common. In some cases, symptoms also include neck pain, nausea, and vomiting.
When a dental infection spreads elsewhere, it’s easy to mistake the issue for something more generalized as opposed to your tooth. Because of the close proximity of dental infections with the airway and brain, doctors may order a CT scan to determine the location of where the infected source originates.
Should You Go To The Hospital?
Who Is An Increased Risk For a Tooth Abscess?
Even though anyone can theoretically die from a tooth infection, there are certain individuals who are at a higher risk of fatal side-effects. Such as:
- Young children
- Individuals with diabetes
- Elderly
- People who are immunocompromised
If you have an immune disease or are more susceptible to illnesses, a severe dental infection can potentially be life-threatening if allowed to go untreated.
How To Treat Infected Teeth?
Most infected teeth can be treated through procedures such as:
- Dental fillings
- Crowns
- Pulpotomies or pulp capping
- Root canal therapy/endodontics
- Surgical extractions
- Antibiotics as part of your restorative/therapeutic procedure
- Deep Cleanings (Periodontal therapy)
Dental infections cannot be treated with antibiotics alone. However, if your infected tooth is severe, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics in conjunction with other procedures to reduce the overall bacterial load inside your body leading up to the treatment. Antibiotics will also help with making your planned procedure more comfortable, as severe infection and swelling can interfere with how effective dental numbing medications (local anesthetic) are during your procedure.
How To Prevent Tooth Infections
The best way to prevent fatal tooth infections is to see your dentist routinely for checkups and cleanings and to treat infected teeth as soon as conditions are diagnosed. Do not wait for a tooth to start hurting before you have it treated. It is not uncommon for cavities to evolve into abscessed teeth without any painful symptoms being present. If a dental abscess is left untreated, it can spread into the head and neck causing serious complications. If you have second thoughts about your dentist’s recommendations for treatment, seek out a second opinion rather than “tough it out” before you see the infection for yourself. Find a local dentist here.
When Are You In The Clear?
Once a cavity or an abscessed tooth has been treated with a filling, root canal, or extraction, you can feel confident knowing you’ve done everything possible to remove that infection from your body. Similarly, areas of gum disease need to be returned back to a non-inflamed, non-bleeding state. Practice good oral hygiene and treat dental issues earlier whenever possible. Don’t second guess your dentist or assume an antibiotic will fix the problem. When in doubt, get a second opinion.
Make your inbox smile!
Subscribe