Tooth And Ear Pain: Causes & Treatment


How closely related are your ear and tooth? It’s common to experience “referred” pain when there’s something like a TMJ/tooth pain/ear infection going on. Referred pain is when you feel like a specific part of your body hurts, but the source of the discomfort is actually coming from an adjacent area.
For example, tooth and ear pain on the same side could actually be caused by tightening in your jaw (TMJ) muscles. Understanding the different types of tooth or ear pain and their warning signs can help you figure out what’s really going on so that you can treat it effectively.
Should I Be Concerned
Tooth and ear pain are probably some of the worst types of pain that a person can experience (some people say that kidney stones are right up there too.) So yes, if there is tooth and ear pain going on, you should be concerned. Fortunately, you probably won’t have to rush off to the emergency room, but you might need to see a dentist or doctor depending on the frequency and severity of your tooth and ear pain.
If it’s your child experiencing tooth and ear pain, you probably want to do everything possible to get them out of pain and into the doctor’s office. Over-the-counter Motrin (ibuprofen) is an anti-inflammatory that helps with swelling, which is a common cause of earaches and toothaches.
Once symptoms start to improve, you can begin to do some detective work to figure out what’s causing it. That way you’ll know which type of doctor to see (dentist/ENT/pediatrician/etc.) and what type of treatment to expect.
Common Causes Of Tooth And Ear Pain
Does tooth and ear pain on the same side flare up at random times, or does it align with things such as swimming and sleeping? Does it happen on both sides?
Depending on your daily habits, exercise routine, and medical history, there are several different reasons behind jaw, tooth, and ear pain. Here are some of the most common scenarios to be aware of:
1) Osteoarthritis
Symptoms
Limited range of motion, stiffness, and pain in your TMJ/jaw joint. Your dentist may be able to observe anatomical irregularities on your full-mouth panoramic X-ray.
Treatment
As prescribed by your rheumatologist. Usually, over-the-counter acetaminophen (Tylenol) is recommended for managing minor discomfort. More severe cases of arthritis may require a prescription.
2) Sinusitis
Symptoms
People with occasional sinusitis are likely to feel as if they have nasal congestion, post-nasal drips, runny nose, sore throat, toothaches, or ear pain (due to the pressure.)
Treatment
Seasonal allergies are typically managed with over-the-counter allergy drugs, decongestants, or anti-histamines. Anti-inflammatory medication can help to dull pain during flare-ups. If sinusitis is moderate to severe, speak to your physician about a prescription-strength medication or antibiotic treatment.
3) Ear Infection
Symptoms
Ear infections tend to cause sharp, constant pain. However, it should be noted that bruxism/grinding/TMJ disorder can cause ear pain that presents itself as an ear infection when it truly is not.
Treatment
Antibiotic therapy is usually the most common treatment for ear infections. Chronic, recurring ear infections in children may require “tubes” being put in their ears to help decrease their frequency.
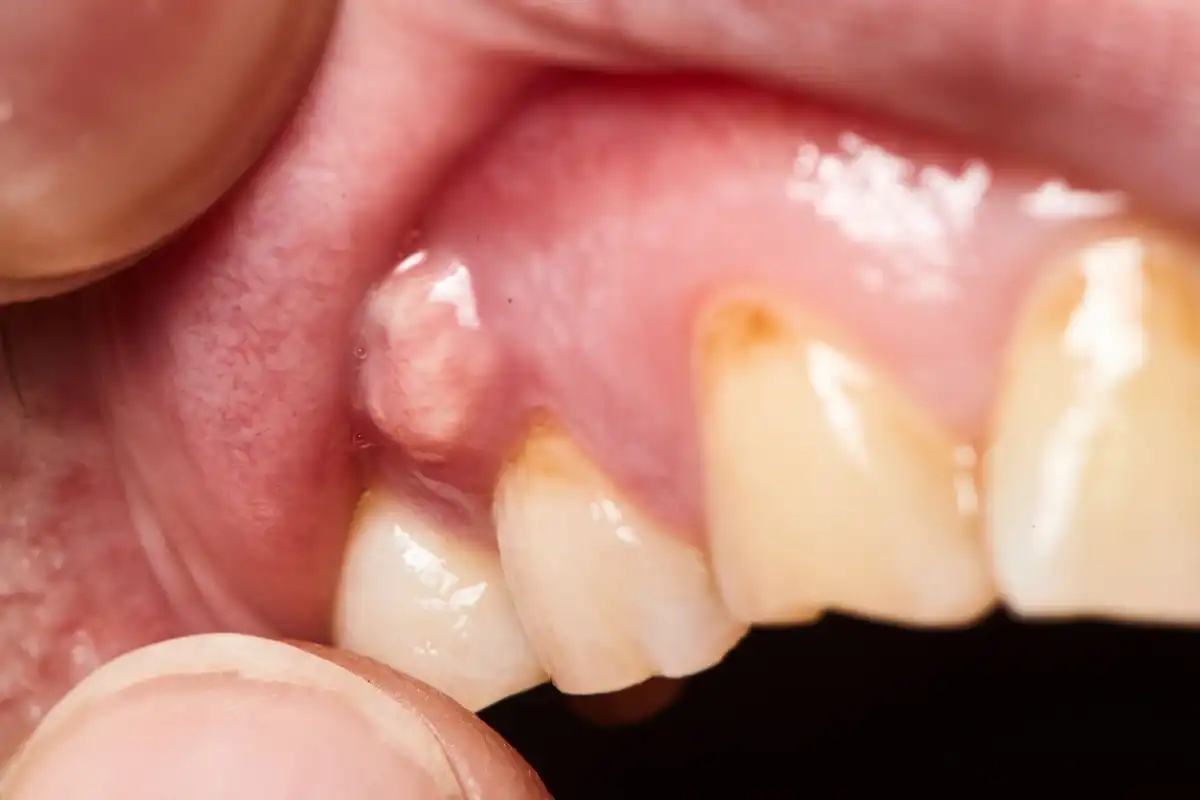
4) Cavities, Periodontal Disease, Or Abscesses
When it comes to tooth and ear pain, the most frequent types of dental issues to cause referred ear pain are those associated with infected upper back teeth (molars). If there is an abscessed tooth, serious gum disease, or a severe area of tooth decay, the pain can seem as if it’s coming from the ear.
Symptoms
This type of tooth pain can range from dull, chronic aches to sharp, acute pain. There may also be swelling along the gums, or visible fistulas (draining abscesses) that give off a salty taste as they come and go. Gums may bleed when you’re brushing and flossing.
Treatment
The best type of treatment will depend on the specific type of tooth infection you have. For periodontitis, that would be a deep cleaning and any other gum therapies. For cavities, you would probably need a filling. Abscessed teeth will typically need endodontic therapy (root canals) if they can be saved. More serious stages of these infections might require a tooth extraction.
5) Teeth Grinding
Symptoms
Sore TMJ, headaches, ear pain, jaw pain, tooth pain, flattened/worn/fractured teeth, and a visible raised line across the sides of the tongue, where teeth meet.
Treatment
Wearing a bite splint or night guard to reduce muscle tension and grinding habits. Possible injectable therapy with products like Botox (which is a natural muscle relaxant.)
6) Swimmer’s Ear (Leading To Ear Infection)
If you have a recreational or competitive swimmer in the family, swimmer’s ear can lead to ear infections in one or both ears.
Symptoms
Fever, pain, drainage, dizziness, loss of hearing, itching, redness.
Treatment
7) Rheumatoid Or Psoriatic Arthritis
Symptoms
Joint pain, TMJ discomfort, limited range of motion, intermittent flare ups.
Treatment
Corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by your rheumatologist.
When To See A Doctor
If you’re fairly certain that the tooth or ear pain is coming from somewhere inside of your mouth, the first professional you want to see is your family dentist. They’ll perform a thorough exam and take either a single-tooth PA X-ray or a full-mouth pano (which shows all of your nasal sinuses, TMJ, and close to your ear.) At that point your dentist will be able to rule out any specific types of dental infections, TMJ disorder, and evaluate the adjacent anatomy for possible causes.
If your pain isn’t related to your teeth or TMJ, the next provider to see would be your primary care physician. They can examine your ears to screen for a possible infection or sinusitis. Or, they may go ahead and refer you directly to a specialist such as an ENT, who is best equipped to treat non-oral-related issues causing ear or tooth pain.
Pain Relief At Home
An over-the-counter anti-inflammatory (such as ibuprofen or Motrin) can provide temporary pain relief if your tooth and ear pain is due to swelling. You can also apply a warm or cold compress to the side of your face that hurts, taking it on and off every 20 minutes.
Seasonal allergy sufferers who tend to develop sinus inflammation may want to speak to their doctor about a regimen of anti-histamines, allergy medications, or other preventative strategies. That way the pressure doesn’t build up over time and push against their teeth or ears. In more severe cases of sinus-induced tooth and ear pain, your physician might recommend daily allergy shots as a preventative strategy.
Overcoming Tooth And Ear Pain
If you have tooth and ear pain on the same side, there’s a really good chance that you have something like TMJ disorder or a sinus infection going on. Since your TMJ, teeth, ears, and sinuses are all so close to each other, it’s common to experience referred pain that is coming from one area or the other.
However, issues such as swimmer’s ear, arthritis, or abscessed teeth can in rare cases cause similar symptoms. If your pain is severe and doesn’t go away through routine home care, speak to your dentist or physician to get an accurate diagnosis and specific treatment plan.
Make your inbox smile!
Subscribe